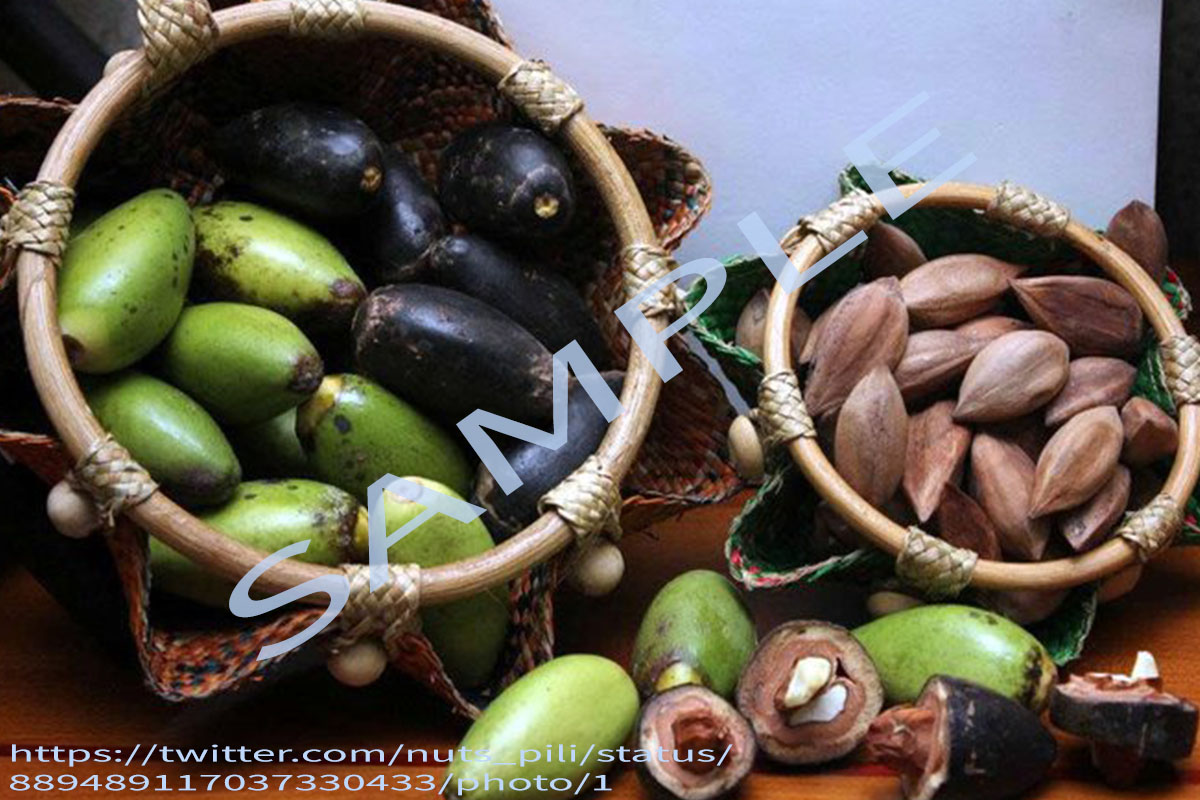MORPHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Home / Bioecology / Morphology
Morphological Characteristics of Pili
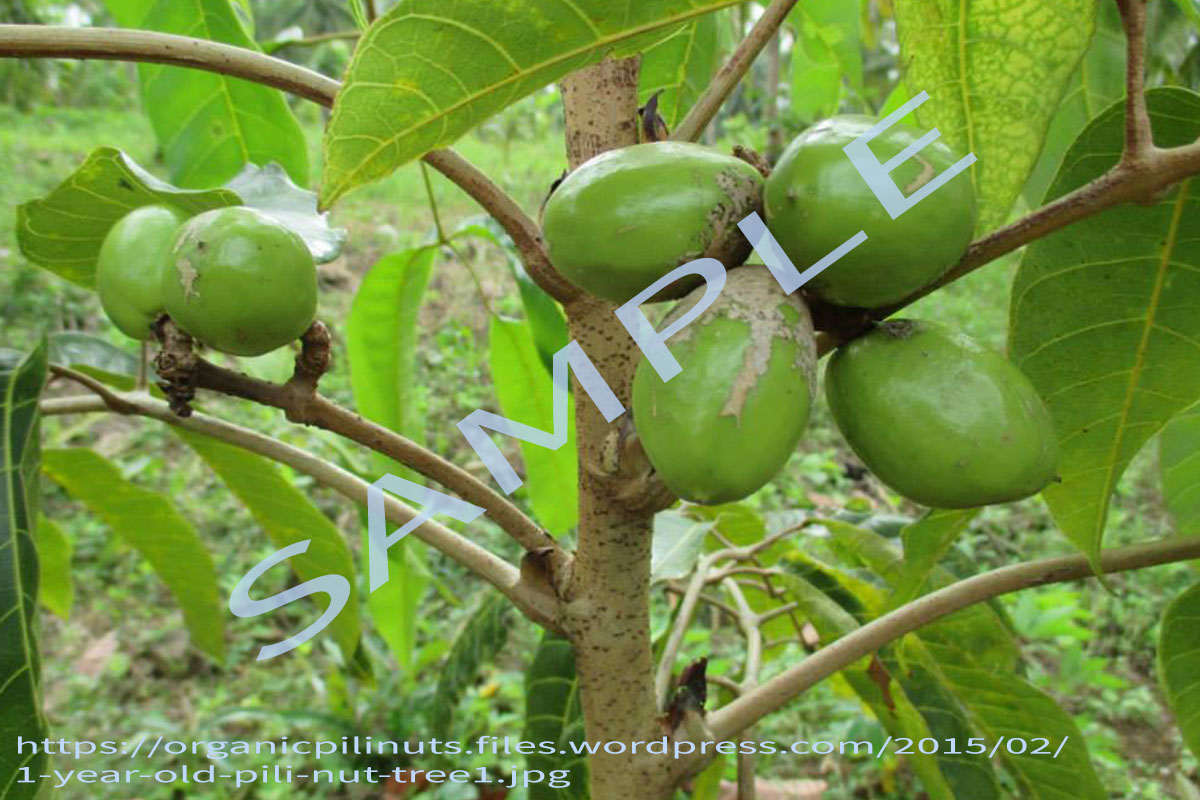
Canarium ovatum Engl. is an attractive, symmetrically shaped evergreen tree, up to 20 m tall and 50 cm in diameter. Stipules persistent, deltoid to lingulate, 5-20 x 3-10 mm. (World Agroforestry.org)
Leaves 2-4-jugate, imparipinnate, spirally arranged, about 40 cm long; leaflets ovate to elliptic, 4-24 x 2-12 cm, stiff, coriaceous, entire, base oblique, rounded to subcordate, apex abruptly acuminate, 8-12 pairs of nerves.
Inflorescence axillary, close together at the ends of branches, narrowly thyrsoid, 3-12 cm long, few flowers; flowers trimerous, unisexual, subsessile, pubescent, up to 12 mm long, calyx cupular, 7 mm long in male, 8-9 mm in female flowers; petals 2 x 1 cm; stamens 6, slightly adnate to the disk and sterile in female flowers; pistil absent in male flowers, 7 mm long in female.
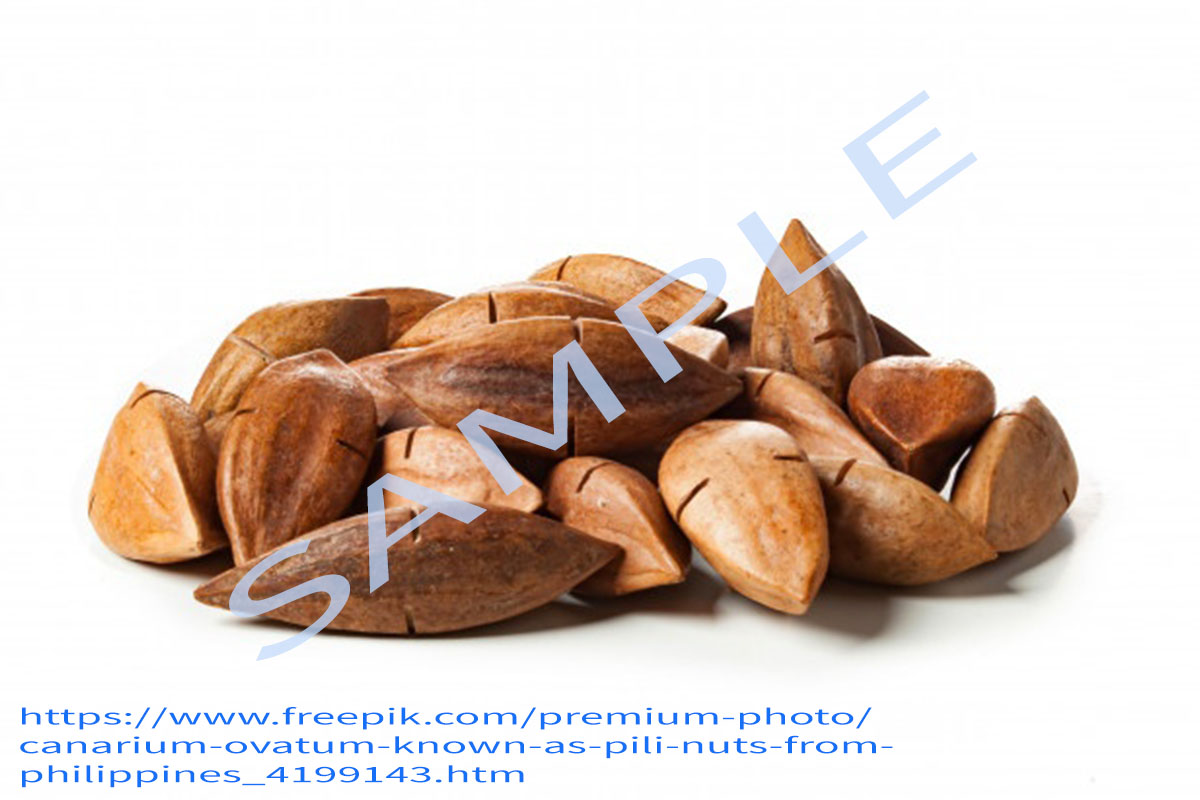
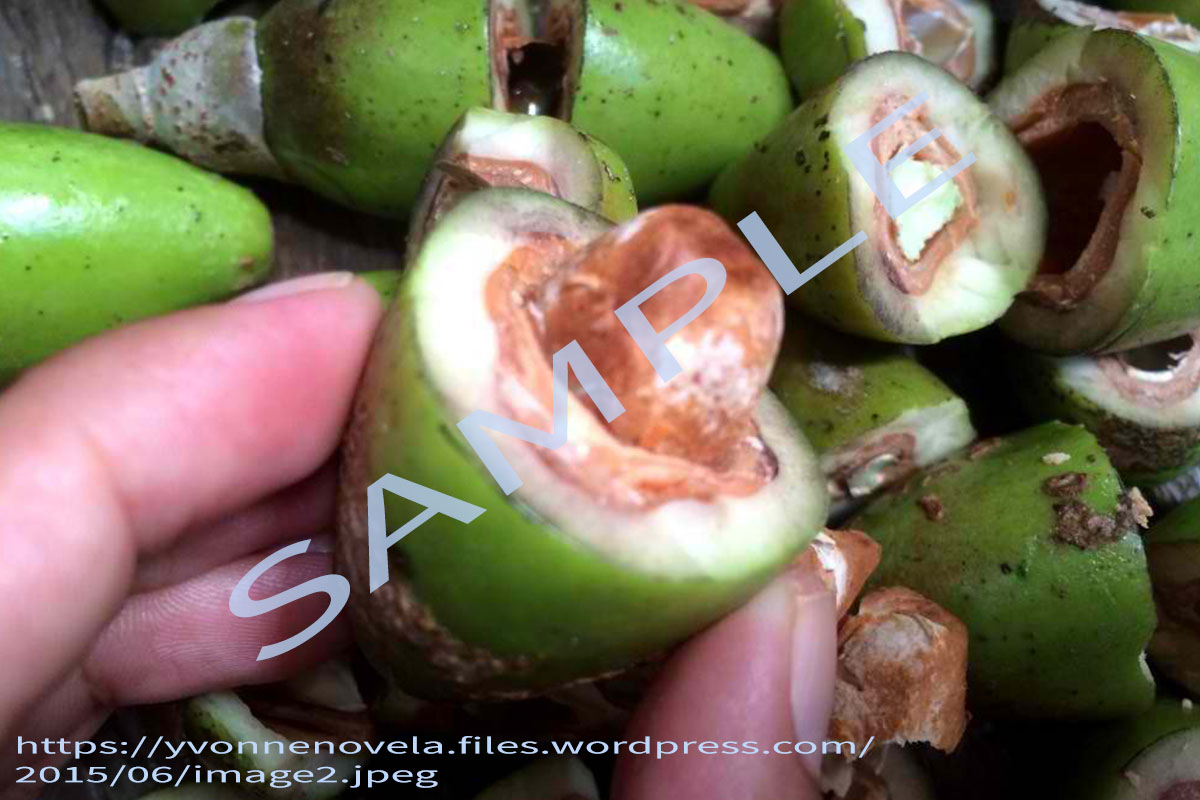
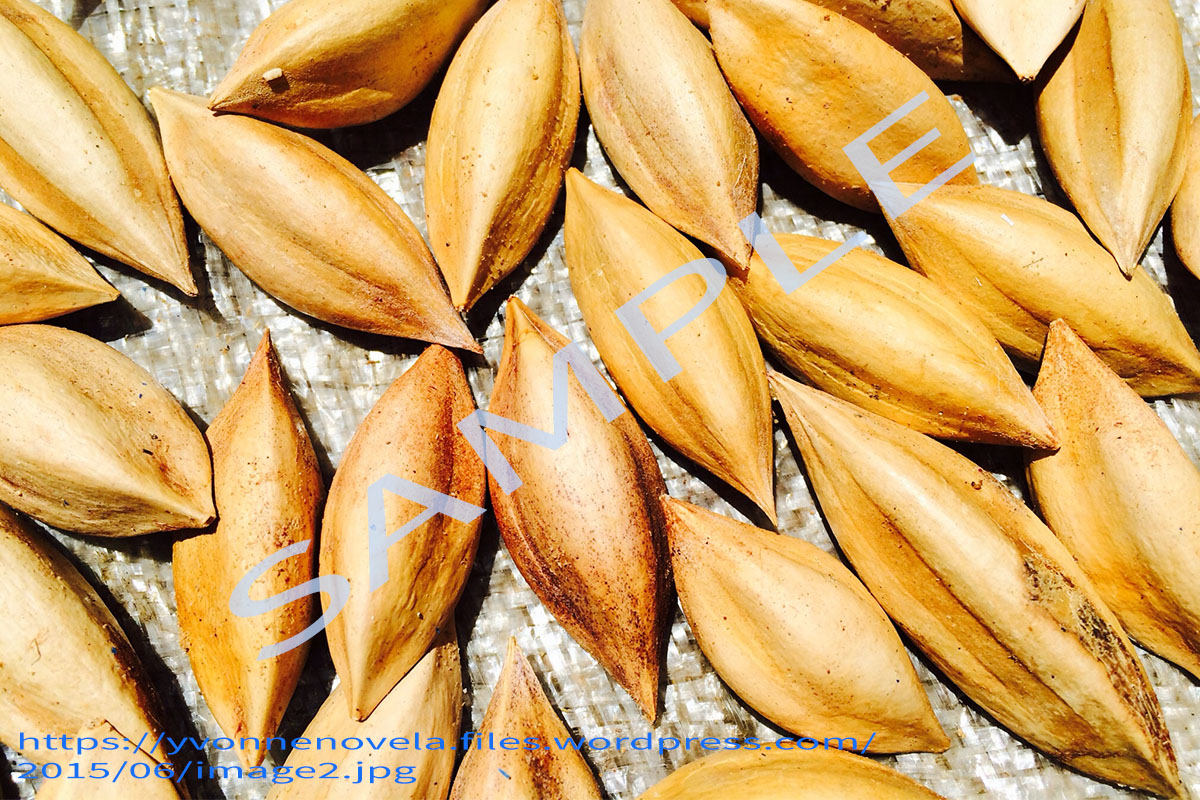
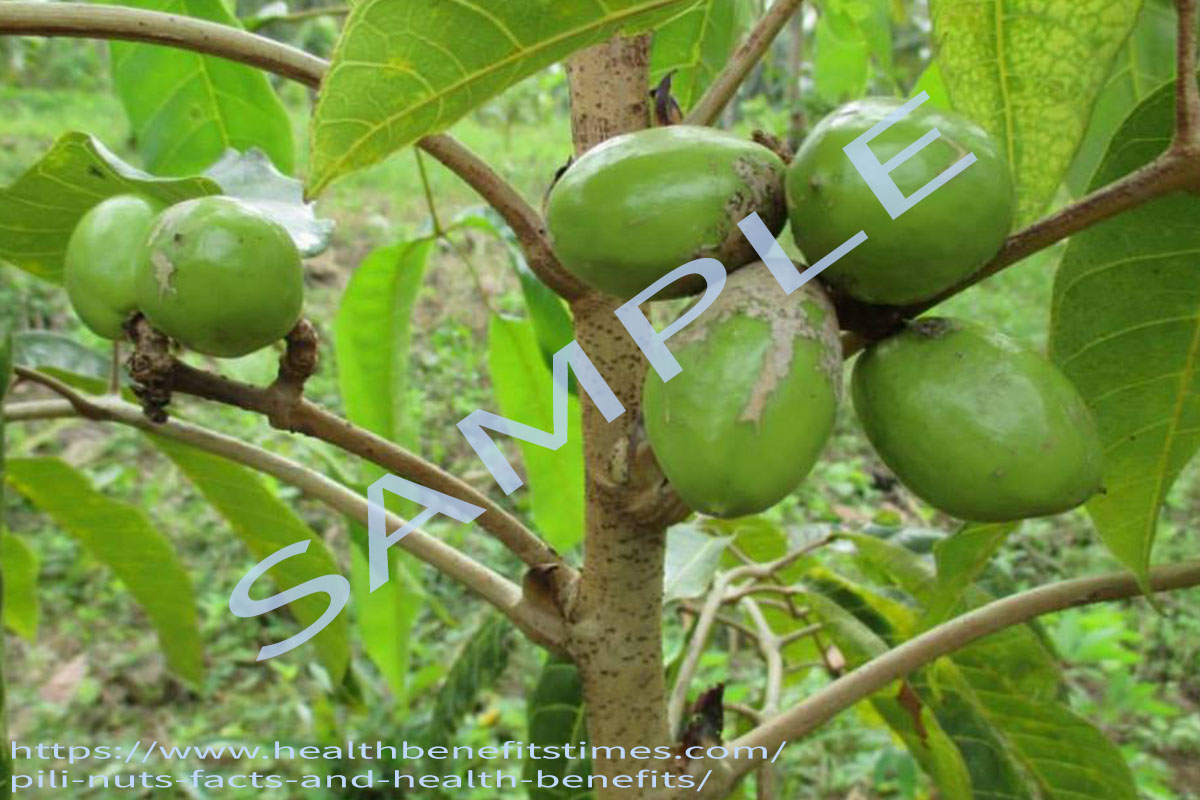
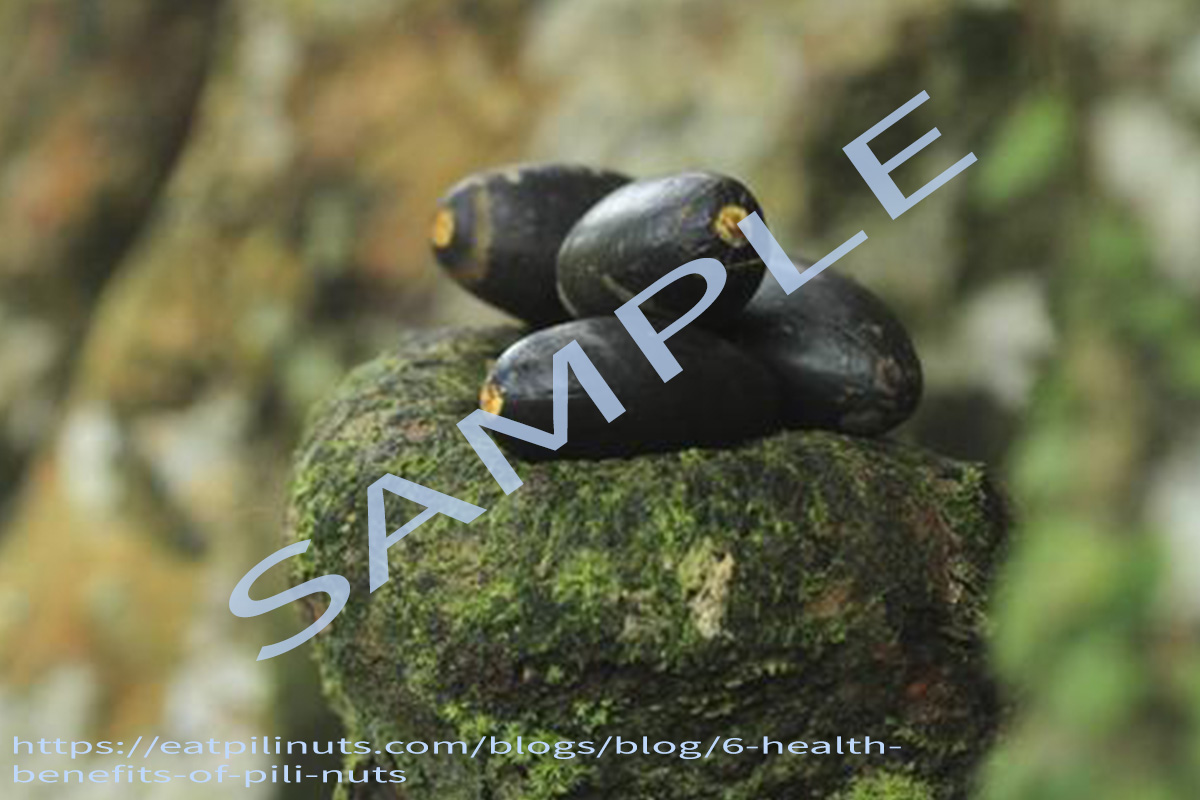
Fruit drupaceous, ovoid to ellipsoid, 3.5-6.25 x 2-2.75 cm, acute, triangular in cross-section; exocarp thin, glabrous, shiny, turning from light green to purplish-black; mesocarp fibrous, fleshy, thick and greenish-yellow in colour; endocarp (shell) elongated, stony, trigonous, pointed at base, blunt or obtuse at apex, tawny to dirty brown, sterile cells strongly reduced. Seed with 1 brown papery seed coat. Much of the kernel weight is made up of the cotyledons, which are about 4.1-16.6% of the whole fruit.
Browse our comprehensive collection of pili varieties and discover its morphological characteristics.